
ERCIM News No.37 - April 1999
Internet Enhancements - Coexistence with ATM
by Magda Chatzaki and Stelios Sartzetakis
The IthACI project - Internet and the ATM: Experiments & Enhancements for Convergence and Integration - aims at contributing to the Multi-Protocol Layer Switching (MPLS) standardization efforts by developing and demonstrating enhanced features in the areas of multicast, QoS and resource management in IPSOFACTO and Tag-Switching, and mobility in a multicast environment. The project is setting up a testbed consisting of three distinct technology islands based on ATM switching technologies of different vendors, which incorporate different approaches for short-cutting IP traffic. NEC’s ‘IPSOFACTO’, CISCO’s ‘Tag Switching’ and ALCATEL’s ‘Yalsa technologies’ are in operation in the test networks in three different countries in Europe, the enhanced features are under development on these technology islands, and their interconnection is planned over a Pan-European ATM wide area network.
Internet technology dominates communications today, with its TCP/IP protocols suite mostly appreciated because of its simplicity and flexibility. Traditional Internet supports only best effort service. However it transforms quickly into a commercial environment demanding support for Quality of Service (QoS). In order to provide means to guarantee QoS in the Internet environment we might increase its complexity by adding protocols for resource management, like RSVP (Resource reSerVation Protocol), so loosing some of its original simplicity. Coming from the Telecom Operators world, ATM has been designed to support different QoS requirements providing simple and clean solutions. IP switching seems to be a promising new approach to combine the speed of ATM switching with the simplicity and flexibility of IP internetworks. The basic idea of IP switching is to use IP network control on top of an ATM switch. MPLS (MultiProtocol Layer Switching) is the standard solution for IP switching proposed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The MPLS standard is currently evolving to cover the areas of Quality of Service and Resource Management, Multicast support and Mobility for IP switching technologies.
QoS and Resource Management Enhancements in Tag Switching aim at providing QoS and Resource Management functionality to the Tag Switching technology and consequently to MPLS. The enhancements to Tag Switching towards QoS and Resource Management are based on the idea of establishing an overall QoS provisioning framework from the viewpoint of a Service Provider. The QoS provisioning framework should provide differentiation between the services in terms of their transfer characteristics and above all differentiation among customers in terms of the services they may request. The framework is compatible with both IntServ and DiffServ approaches for QoS provisioning emerging in the Internet. It entails two aspects:
- definition of a set of discrete Service Classes (SCs) for requesting QoS-based services
- definition of a suitable architecture and protocols required for supporting the provisioning of the defined QoS-based services in the network.
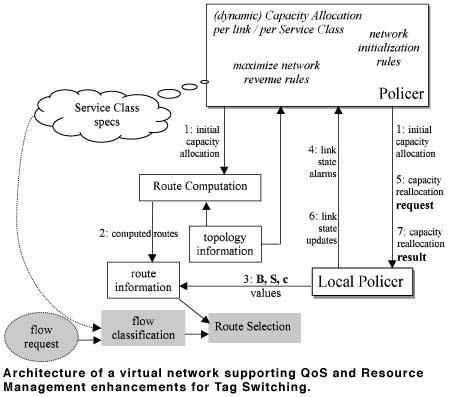
The basic idea underlying this QoS framework is to create and dynamically manage a virtual topology induced to the physical one for allowing segregation of network resources (ie bandwidth) to the different SCs, cost-effectively and according to business policies. We name this virtual topology soft-network. The soft-network is used to configure and reserve the available network resources according to the characteristics of the supported SCs. Our architecture includes a mechanism that supports multiservice, multipath routing in Tag Switching (MPLS) capable networks. It supports initial allocation and dynamic reallocation of network resources whenever necessary for multiple SCs. We consider a network that supports a number of SCs with different QoS guarantees. In our approach, network resources are initially allocated to the different SCs according to the administrative policies of the network operator. This means that appropriate virtual networks are created to accommodate the traffic demands of the SCs according to their QoS characteristics. ICS-FORTH is mainly involved in this task and together with Algosystems S.A. develops the architecture shown in the figure in order to support the QoS and Resource Management enhancements for Tag Switching.
QoS and Resource Management Enhancements in IPSOFACTO include several tasks. The existing flow detection mechanisms in the IPSOFACTO architecture are being enhanced further with an real time protocol (RTP) flow detection mechanism. It should be noted here that RTP applications are very important, as they are actually real-time and therefore require a better service than traditional data applications. Further flow differentiation among the RTP flows is done using some clever assignment of flows with specific RTP profiles that will be mapped to the appropriate ATM switch service classes treatment. The Resource Management enhancements first task is the development of a common prototype for the co-existence of a topology-driven unicast-oriented IP switching technique (MPLS) and a flow-driven IP switching technique (NECs IPSOFACTO). Interoperability and resource management issues involved with their co-existence will be studied. The second task is the design and implementation of a Flow Management Information Base (Flow MIB) to be used with NECs IPSOFACTO. The Flow MIB provides information on past and present flows.
For the Multicast Service enhancements we apply MPLS-style shortcut techniques to IP multicast in order to optimize the network without modifying the end-user environment and the existing IP multicast protocols. The shortcut point-to-multipoint ATM connections will follow dynamically the tree topology changes that are the result of IP hosts joining or leaving the group. Among various Multicast Routing Protocols being implemented and standardised IthACI selected the PIM-SM (Protocol Independent Multicast - Sparse Mode) because of the scalability limitations of the others. PIM-SM is deployed as the Multicast Routing Protocol in all three IthACI islands. However, each island uses its own method to do the mapping of multicast streams onto layer 2 connections. Besides correct interworking of IP multicast and IP switching in the separate islands, the goal is to demonstrate the interoperability between Alcatels, NECs and Ciscos multicast solutions, either on layer 2 or layer 3.
The enhancements for mobility in a multicast environment follow the approaches supported by the IETF standards. The realisations in IthACI will conform to appropriate ‘Requests for Comments’ as long as they are available. Some ongoing work in IETF will also be considered and related Internet drafts are examined and applied accordingly. Two major schemes are possible to make the multicast service available to a mobile node. While away from home, a Mobile Node may be allowed to exercise its role either as if it were a logical entity in the home network or a logical entity in its current foreign network. In the first scheme, the Home Agent acts as the logical point of service. In the second scheme, the Mobile Node has to use a temporary co-located care-of-address to fulfil its role in the multicast scenarios.The demand for higher throughput IP networks is huge. IthACI focuses on applying IP switching technologies to better satisfy this demand. Most of the major switch/router manufacturers have already announced MPLS support in their products, and will deliver by years end. IthACI also examines MPLS extensions and applicability to IP over DWDM (Dense Wave Division Multiplexing) layered networks.
IthACI project partly funded by ACTS started March 1998. The other consortium members are AlgoSystems S.A., University of Surrey, ABT, GMD-Fokus, CISCO Systems S.A., NEC Europe Ltd. and IMEC. Further information can be found at: http://www.algo.com.gr/acts/ithaci/
Please contact:
Stelios Sartzetakis - ICS-FORTH
Tel: +30 81 39 1727
E-mail: stelios@ics.forth.gr
Magda Chatzaki - ICS-FORTH
Tel: +30 81 39 1723
E-mail: magda@ics.forth.gr