Digital Libraries and Information Retrieval
by Reginald Ferber and Ulrich ThielDigital Libraries (DL) is a metaphor for access to collections of electronic documents through a network. The classic research area dealing with the electronic search for documents is Information Retrieval. During the last 30 years the topic of this discipline evolved from electronic catalogs to the management of fulltext and multi-media documents. So, from a first viewpoint Digital Libraries and Information Retrieval are not that different. The challenge of Digital Library research is the framework in which it evolves: Information Retrieval has to leave the controlled and uniform conditions of professional information providers. It is confronted with a vast variety of servers, formats, indexing strategies, and query mechanisms. One of the main topics in DL research will be to cope with this heterogeneity. 'Multimedia Information Retrieval Dialog Techniques, the Information Retrieval department of the GMD-Insitute for Integrated Publication and Information Systems, is working on several aspects of this problem.
Most present day Document Retrieval Systems employ specialized personnel to index documents. However, many providers of repositories for electronic documents are not able to use this successful but expensive method. An alternative is the use of automated indexing tools for full text documents. They are faster and less expensive and they can take advantage of structural information (like HTML or SGML tags) included in electronic documents. In addition they can incorporate specific views of specific users. GMD Institute for Integrated Publication and Information Systems is developing an automated indexing system for multimedia documents based on a Bayesian inference network. Such a network uses probabilistic estimates on multiple paths of evidence. In this way partial evidence from various sources can be combined to a document's overall estimation of relevance for a specific query. In addition our system includes a set of rules, which can be activated to detect a specific way of occurrence of an index term, or a specific feature in a digitized image and consequently ascribe an appropriate indexing concept.
Query Interpretation and Expansion
A good query has to be general enough to cover all relevant documents and specific enough to select only relevant ones. To achieve a high specificity we use the rules defined for the indexing tool and, in addition, a set of domain specific rules. These rules are managed by an abductive system, ie a system for hypothetical reasoning. It constructs the possible interpretations of query terms corresponding to alternative paths in the inference network and negotiates them with the user. In this way the user is able to select his/her intended interpretation of an unstructured query. Another way to enhance a query is to add related terms either as a substitution for or as an addition to existing query terms. Such related terms can be synonyms, associatively related terms, more general or more specific terms. To find such related terms we use co-occurrence analysis based on large corpora of documents of the respective domain. This corpus based method allows the fast creation of such associative thesauri which are specific to a given domain and time.
Dialog Management
Most retrieval sessions consist of a series of searches each based on the results of previous attempts. During this interaction the user elaborates his/her query. For many inexperienced users the cognitive load of managing the search and scanning the documents found is very high. In a Digital Libraries environment the situation will be worse due to the heterogeneity of the various systems and servers. To help users in this situation we develop a Dialog Management System that keeps track of the interaction; it is able to offer context specific interpretations of user actions and propose further steps in a context sensitive way. The system is based on the linguistic dialog model COR (Conversational Roles) and generic strategies for typical retrieval situations.
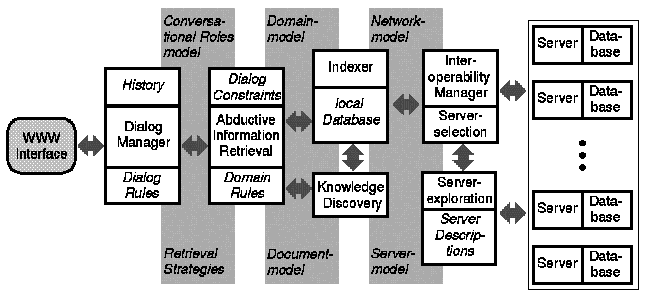
Distributed Digital Library Retrieval Model. The theoretical concepts are displayed in the background,
the modules of the system are given in the foreground.
(Some related work was described in: ERCIM News No. 18, 1994; pp.15-16, 21-22, 26-27).
Server Selection
A special problem of Digital Libraries is the selection of appropriate servers
for a given query. This is a kind of 'Meta Search'. Within the ERCIM project
on Digital Libraries we plan to develop a system in which the remote servers
are described in an appropriate model of servers. This model will include
static descriptions like retrieval engines available, format of queries,
domain of the server, average load, prices, network bandwidths, etc. In
addition we plan to use knowledge discovery methods to get information about
a server: samples of documents will be analyzed with the indexing tool to
characterize a server. These samples can either be drawn by chance or as
response to a broad query characterizing a domain.
Please contact:
Ulrich Thiel - GMD
Tel: +49 6151 869 855
E-mail: Ulrich.Thiel@gmd.de
