This issue in pdf Archive: Next issue: Next Special theme: |
|
|||||
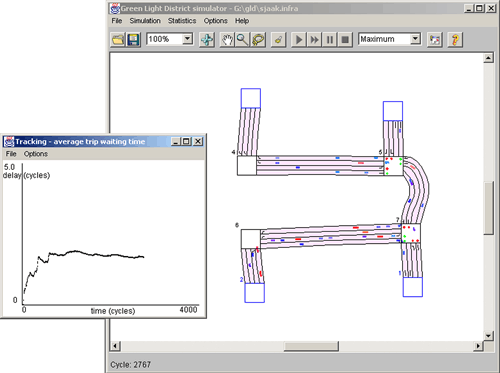
Intelligent Traffic Light Controlby Marco Wiering Growing numbers of road users and the limited resources provided by current infrastructures lead to ever increasing traveling times. The Intelligent Traffic Light Control project pursued at Utrecht University aims at diminishing waiting times before red traffic lights in a city. Traffic in a city is very much affected by traffic light controllers. When waiting for a traffic light, the driver looses time and the car uses fuel. Hence, reducing waiting times before traffic lights can save our European society billions of Euros annually. To make traffic light controllers more intelligent, we exploit the emergence of novel technologies such as communication networks and sensor networks, as well as the use of more sophisticated algorithms for setting traffic lights. Intelligent traffic light control does not only mean that traffic lights are set in order to minimize waiting times of road users, but also that road users receive information about how to drive through a city in order to minimize their waiting times. This means that we are coping with a complex multi-agent system, where communication and coordination play essential roles. Our research has led to a novel system in which traffic light controllers and the behaviour of car drivers are optimized using machine-learning methods. Our idea of setting a traffic light is as follows. Suppose there are a number of cars with their destination address standing before a crossing. All cars communicate to the traffic light their specific place in the queue and their destination address. Now the traffic light has to decide which option (ie, which lanes are to be put on green) is optimal to minimize the long-term average waiting time until all cars have arrived at their destination address. The learning traffic light controllers solve this problem by estimating how long it would take for a car to arrive at its destination address (for which the car may need to pass many different traffic lights) when currently the light would be put on green, and how long it would take if the light would be put on red. The difference between the waiting time for red and the waiting time for green is the gain for the car. Now the traffic light controllers set the lights in such a way to maximize the average gain of all cars standing before the crossing. To estimate the waiting times, we use 'reinforcement learning' which keeps track of the waiting times of individual cars and uses a smart way to compute the long term average waiting times using dynamic programming algorithms. One nice feature is that the system is very fair; it never lets one car wait for a very long time, since then its gain of setting its own light to green becomes very large, and the optimal decision of the traffic light will set his light to green. Furthermore, since we estimate waiting times before traffic lights until the destination of the road user has been reached, the road user can use this information to choose to which next traffic light to go, thereby improving its driving behaviour through a city. Note that we solve the traffic light control problem by using a distributed multi-agent system, where cooperation and coordination are done by communication, learning, and voting mechanisms. To allow for green waves during extremely busy situations, we combine our algorithm with a special bucket algorithm which propagates gains from one traffic light to the next one, inducing stronger voting on the next traffic controller option.
We have implemented the 'Green Light District', a traffic simulator in Java in which infrastructures can be edited easily by using the mouse, and different levels of road usage can be simulated. A large number of fixed and learning traffic light controllers have already been tested in the simulator and the resulting average waiting times of cars have been plotted and compared. The results indicate that the learning controllers can reduce average waiting times with at least 10% in semi-busy traffic situations, and even much more when high congestion of the traffic occurs. We are currently studying the behaviour of the learning traffic light controllers on many different infrastructures in our simulator. We are also planning to cooperate with other institutes and companies in The Netherlands to apply our system to real world traffic situations. For this, modern technologies such as communicating networks can be brought to use on a very large scale, making the necessary communication between road users and traffic lights possible. Please contact: |
|||||